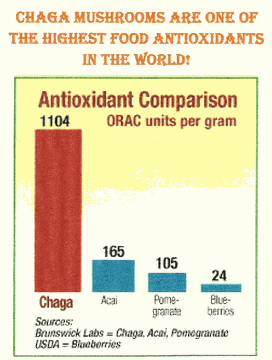
Chaga is one of the highest food antioxidants in the
world!
Buy pure wild harvested Chaga Mushroom click here
Chaga (Scientific Name: Inonotus Obliquus)
Chaga is the most powerful sought after mushroom on earth.
It’s one of the highest, if not the highest, antioxidants in
the world and it’s documented extensively for having
numerous health benefits, but it’s publicized mostly as an
anti-cancer.
Antioxidants
Antioxidants are substances that protect cells from the
damage caused by unstable molecules known as free radicals.
Free radical damage can lead to cancer. Antioxidants
interact with and stabilize free radicals and prevent some
of the damage free radicals might otherwise cause. Examples
of antioxidants include beta-carotene, lycopene, vitamins A,
C and E and other substances. Beta-carotene is found in many
foods that are orange in color, including Chaga.
Anti-Cancer
Betulinic acid, a constituent of
Chaga, is cytotoxic and
triggers apoptosis through a direct effect on the
mitochondria of cancer cells. Other apoptosis-inducing
factors result in cleavage of caspases and nuclear
fragmentation. Like many medicinal mushrooms, Chaga is rich
in beta glucans, which have immunomodulating activities.
Beta glucans bind to Complement Receptor 3 (CR3) that allows
the immune cells to recognize cancer cells as “non-self” A
hot water extract of Chaga exhibited inhibitory and
proapoptotic actions against colon cancer cell proliferation
via up-regulation of Bax and caspase-3 and down-regulation
of Bcl-2. For more information on betulinic acid, please go
to our Science & Research Tab and read the following
Elsevier Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters on New
ionic derivatives of betulinic acid as highly potent
anti-cancer agents, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center,
and Developing Novel Derivatives of Betulinic Acid for
Fighting HIV.
In addition to being used as an anti-cancer, Chaga has
demonstrated anti-HIV, antibacterial, anti-malarial,
anti-inflammatory and anthelmintic properties. Chaga is also
antiviral, antifungal, antimicrobial and anti-Candida. Chaga
is an immune system modulator as well as an adaptogen and
has the highest level of superoxide dismutase or (SOD)
detected in any food or herb in the world.
Anti-HIV
In 2005, published in The Pharmacological Potential of
Mushrooms by Ulrike Lindequist et al., Water-soluble lignins
isolated from Chaga, inhibited HIV protease with an IC 50
value of 2.5 mg ml_1. . Immunostimulation, other effects of
the polysaccharide–protein complexes contribute to the
antiviral activity, e.g. inhibition of binding of HIV-1
gp120 to immobilized CD4 receptor and of reverse
transcriptase activity of viruses. Inhibition of HIV-1
reverse transcriptase was caused by velutin, a ribosome
inactivating protein from Flammulina velutipes (M. A.
Curtis: Fr.) P. Karst., as well. A total of 85% of
responders reported an increased sense of well-being with
regard to various symptoms and secondary diseases caused by
HIV. Twenty patients showed an increase in CD4þ cell counts
to 1.4–1.8 times and eight patients a decrease to 0.8–0.5
times.
Antibacterial
Chaga kills or inhibits growth or replication by destroying
or suppressing reproduction of bacteria. The following are
some properties in Chaga that are antibacterial: Betulinic
Acid, copper, flavonoids, inotodiol, lanosterol, magnesium,
melanin, pantothenic acid, phytonutrients, polysaccharides,
saponins, selenium, sterols, tripeptides, triterpenes and
zinc.
Anti-Malarial
There are many active constituents in Chaga that make it
antimalarial, but the main biological activities are
betulinic acid, saponins and triterpenes.
Anti-Inflammatory
The anti-inflammatory and pain relieving properties of Chaga
are thought to be the inhibition of nitric oxide synthase (iNOS)
and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). An extract of Chaga reduced
the oxidative stress in lymphocytes from patients with
inflammatory bowel disease.
Anthelmintic Properties
There are many active constituents in
Chaga that make it
anthelmintic, but the main biological activities are
betulinic acid, saponins and triterpenes.
Antiviral
There are many active constituents in
Chaga that make it
antiviral, but the main biological activities are betulinic
acid, saponins and triterpenes.
Antifungal
The following properties make
Chaga an antifungal: beta
glucans, betulinic acid, copper, enzymes, flavonoids,
lanosterol, manganese, magnesium, pantothenic acid, phenols,
polysaccharides, saponins, selenium, sterols, trametenolic
acid, triterpenes, triterpenoids and zinc.
Antimicrobial
Antimicrobial properties in Chaga are amino acids, betulinic
acid, chitin, copper, enzymes, flavonoids, inotodiols,
lanosterol, manganese, magnesium, melanin, phenols,
phytonutrients, polysaccharides, potassium, saponins,
selenium, sterols, trametenolic acid, tripeptides,
triterpenes, triterpenoids, vanillin and zinc.
Anti-Candida
Chaga promotes and protects the functions of the liver which
busily processes Candida toxins.
Chaga has properties that help to lower cholesterol,
inflammation and blood pressure levels through sterols and
triterpenes. Chaga contains B and D vitamins and lots of
protein which promote relief from stress, depression and
fatigue which Candida sufferers deal with.
Immune System Modulator
Chaga has potent immune supporting properties. Chaga is a
rich source of beta glucans, and polysaccharides that are
essential nutrients for the immune system. These
polysaccharides have strong anti-inflammatory and immune
balancing properties, enhancing the body’s ability to
produce natural killer (NK) cells to battle infections.
These polysaccharides are considered to be the primary
active constituents of Chaga, at least from an immunological
perspective. Upon ingestion, a range of secondary
metabolites are produced, many of which are highly active as
potent immune modulators. Chaga polysaccharides effectively
promote macrophage (white blood cell) activation through the
MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways, suggesting that Chaga
polysaccharides help regulate the immune response of the
body.
Adaptogen
Chaga is an adaptogen, which means its compounds increase
the body's ability to adapt to stress, fatigue, anxiety and
changing situations.
Superoxide Dismutase (SOD)
Chaga has the highest level of superoxide dismutase or (SOD)
detected in any food or herb in the world! Superoxide
Dismutase (SOD) is an enzyme that repairs cells and reduces
the damage done to them by superoxide, the most common free
radical in the body. SOD is found in both the dermis and the
epidermis, and is key to the production of healthy
fibroblasts (skin-building cells).
Studies have shown that SOD acts as both an antioxidant and
anti-inflammatory in the body, neutralizing the free
radicals that can lead to wrinkles and precancerous cell
changes. Researchers are currently studying the potential of
superoxide dismutase as an anti-aging treatment, since it is
now known that SOD levels drop while free radical levels
increase as we age.
Superoxide Dismutase helps the body use zinc, copper, and
manganese. There are two types of SOD: copper/zinc (Cu/Zn)
SOD and manganese (Mn) SOD. Each type of SOD plays a
different role in keeping cells healthy. Cu/Zn SOD protects
the cells’ cytoplasm, and Mn SOD protects their mitochondria
from free radical damage.
Superoxide Dismutase has also been used to treat arthritis,
prostate problems, corneal ulcers, burn injuries,
inflammatory diseases, inflammatory bowel disease, and
long-term damage from exposure to smoke and radiation, and
to prevent side effects of cancer drugs. In its topical
form, it may help to reduce facial wrinkles, scar tissue,
heal wounds and burns, lighten dark or hyperpigmentation,
and protect against harmful UV rays.
Active Constituents of Chaga
The active constituents of Chaga are thought to be a
combination of Amino Acids, Beta Glucans, Betulinic Acid,
Calcium, Chloride, Copper, Dietary Fiber, Enzymes,
Flavonoids, Germanium, Inotodiols, Iron, Lanosterol,
Manganese, Magnesium, Melanin, Pantothenic Acid, Phenols,
Phosphorus, Phytonutrients, Polysaccharides, Potassium,
Saponins, Selenium, Sodium, Sterols, Trametenolic Acid,
Tripeptides, Triterpenes, Triterpenoids, Vanillic Acid,
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine), Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin), Vitamin B3
(Niacin), Vitamin D2 (Ergosterol), Vitamin K and Zinc.
Amino Acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that combine to form
proteins. Amino acids and proteins are the building blocks
of life. When proteins are digested or broken down, amino
acids are left. The human body needs a number of amino acids
to:
• Break down food • Grow • Repair body tissue • Perform many
other body functions
Beta Glucans
Beta glucans are used for high cholesterol, diabetes,
cancer, and HIV/AIDS. Beta glucans are also used to boost
the immune system in people whose body defenses have been
weakened by conditions such as chronic fatigue syndrome, or
physical and emotional stress; or by treatments such as
radiation or chemotherapy. Beta glucans are also used for
colds (common cold), flu (influenza), H1N1 (swine) flu,
allergies, hepatitis, Lyme disease, asthma, ear infections,
aging, ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease, fibromyalgia,
rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis.
Betulinic Acid
Betulinic acid is a natural pentacyclic lupane-type
triterpene that is found in Chaga, as well as other various
plants, including birch trees. This compound and its
derivatives possess many favorable biological properties
such as anti-cancer, anti-HIV-1 (human immunodeficiency
virus type-1), antibacterial, anti-malarial,
anti-inflammatory, and anthelmintic activities. Betulinic
acid was initially known for its high cytotoxicity against
human melanoma cancer cells, but later studies also suggest
this compound being a broad inhibitor of other cancerous
tumors including aneuroectodermal tumors (such as
neuroblastoma, medulloblastoma, glioblastoma and Ewing’s
sarcoma), brain-tumors, human gliomas, leukemia, human colon
carcinoma and human prostate adenocarcinoma, head and neck
squamous carcinoma cells, lung, colorectal, breast, and
cervical cancer.
Calcium
One of the most abundant minerals in the human body, calcium
accounts for approximately 1.5% of total body weight. Bones
and teeth house 99% of the calcium in the body, while the
remaining 1% is distributed in other areas.
Calcium is best known for its role in maintaining the
strength and density of bones. In a process known as bone
mineralization, calcium and phosphorus join to form calcium
phosphate. Calcium phosphate is a major component of the
mineral complex (called hydroxyapatite) that gives structure
and strength to bones.
Calcium also plays a role in many physiological activities
not related to bones including blood clotting, nerve
conduction, muscle contraction, regulation of enzyme
activity, and cell membrane function. Because these
physiological activities are essential to life, the body
utilizes complex regulatory systems to tightly control the
amount of calcium in the blood so that calcium is available
for these activities. As a result, when dietary intake of
calcium is too low to maintain normal blood levels of
calcium, the body will draw on calcium stores in the bones
to maintain normal blood concentrations, which, after many
years, can lead to osteoporosis.
Chloride
Chloride is one of the most important electrolytes in the
blood. It helps keep the amount of fluid inside and outside
of your cells in balance. It also helps maintain proper
blood volume, blood pressure, and pH of your body fluids.
Copper
Copper is a natural element that is an essential
micronutrient to ensure the well-being of all aerobic life
forms. It plays a vital part in the development and
performance of the human nervous and cardiovascular systems,
as well as the skin, bone, immune and reproductive systems,
including gene transcription. Copper can also inhibit the
growth of microbes, thus providing a measure of protection
against harmful germs and bacteria in many environments.
Copper has been found useful for its healing powers—largely
due to its antibacterial and antifungal properties—in the
treatment of wounds and skin diseases. Present in our bodies
from conception, copper helps form a developing infant’s
heart, skeletal and nervous systems, as well as arteries and
blood vessels. Copper continues to play a vital role as we
age – keeping our hair and skin in good condition while
repairing and maintaining connective tissue in our hearts
and arteries. It also facilitates absorption and utilization
of iron and enables cells to use the energy present in
carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
Dietary Fiber
Dietary fiber intake provides many health benefits. However,
average fiber intakes for US children and adults are less
than half of the recommended levels. Individuals with high
intakes of dietary fiber appear to be at significantly lower
risk for developing coronary heart disease, stroke,
hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and certain
gastrointestinal diseases. Increasing fiber intake lowers
blood pressure and serum cholesterol levels. Increased
intake of soluble fiber improves glycemia and insulin
sensitivity in non-diabetic and diabetic individuals. Fiber
supplementation in obese individuals significantly enhances
weight loss. Increased fiber intake benefits a number of
gastrointestinal disorders including the following:
gastroesophageal reflux disease, duodenal ulcer,
diverticulitis, constipation, and hemorrhoids. Prebiotic
fibers appear to enhance immune function. Dietary fiber
intake provides similar benefits for children as for adults.
Enzymes
Enzymes are energized protein molecules found in all living
cells. They catalyze and regulate all biochemical reactions
that occur within the human body. They are also instrumental
in digestion. They break down proteins, fats, carbohydrates
and fiber making it possible to benefit from the nutrients
found in those foods while removing the toxins. Enzymes turn
the food we eat into energy and unlock this energy for use
in the body. Their presence and strength can be determined
by improved blood and immune system functions.
Flavonoids
Flavonoids are polyphenols abundantly found in fruits,
vegetables, and herbs. They are a diverse group of
phytochemicals, exceeding four thousand in number. From
human nutrition perspective, flavonoids are important
components of a healthy diet because of their antioxidant
activity. Nevertheless, the antioxidant potency and specific
effect of flavonoids in promoting human health varies
depending on the flavonoid type (chemical, physical, and
structural properties). Among the potent antioxidant
flavonoid types are quercetin, catechins and xanthohumol.
Flavonoid science is a research area rapidly gaining deeper
insight on the health benefit and chemical property of
flavonoids.
Beneficial effects of flavonoids on human health are partly
explained by their antioxidant activity. Because of the
antioxidative property, it is suggested that flavonoids may
delay or prevent the onset of diseases (such as cancer)
induced by free radicals. They also inhibit low density
lipoprotein (LDL) oxidation by free radicals. Flavonoids
have been reported to have negative correlation with
incidence of coronary heart disease. Furthermore, flavonoids
have anti-bacterial, anti-viral, anti-tumor,
anti-inflammatory, antiallergenic, and vasodilatory effect.
They also inhibit platelet aggregation.
Germanium
Nutritionally, the natural element germanium has been known
to aid in the prevention of cancer and AIDS. Certain
compounds of germanium have toxic effects against certain
bacteria. In its organic form, germanium is being hailed as
one of the greatest new developments in the nutritional
treatment of cancer. The estimated daily intake for
germanium is 1 mg. Germanium has been reported to improve
the immune system, boost the body's oxygen supply, make a
person feel more energetic, and destroy damaging free
radicals. Germanium also protects against radiation.
Organic germanium is a biological-response modifier. This
means it enables the body to change its response to tumors,
which has therapeutic benefits. Germanium does not directly
attack cancer cells, but stimulates the body's immune
system, making it effective in the treatment of cancer as
well as other degenerative diseases.
A number of human cancer trials have been conducted with
organic germanium. A summary of Phase I and Phase II human
clinical trials reveals that orally administered organic
germanium induces interferon production, restores previously
impaired immune response, and has shown extremely low
toxicity.
Inotodiol
Inotodiol and trametenolic acid are considered to be the
main bioactive compounds of the fruiting body of the
mushroom. These compounds show various biological
activities, including anti-tumour, anti-viral, hypoglycaemic,
anti-oxidant and cyto-protective. Inotodiol has shown
activity against influenza (flu) viruses A and B and various
cancer cells. Inotodiols extracted from Chaga exhibit
anti-tumor properties, destroying Walker 256 Carcinosarcoma
cancer cells and MCF-7 human adenocarcinoma mammary cells.
Institutional studies at the University of Tokyo, Japan have
determined the effective destruction of certain cancerous
carcinosarcomas and mammary adenocarcinomas.
Iron
Iron is a mineral essential for life. It is present in every
living cell and is necessary for the production of
hemoglobin (primary component of red blood cells), myoglobin
(major protein of muscle cells), and certain enzymes. Iron,
along with calcium, are the two major deficiencies of
American women (one of the reasons due to menstruation and
bleeding), and this deficiency can cause weakness, inability
to concentrate, the susceptibility to infection, impaired
performance, and in general, ill health. Other people at
risk of iron deficiency include dieters, vegetarians and
athletes. Calcium and copper must be present for iron to
function properly, and ascorbic acid (vitamin c) enhances
absorption. Iron is necessary for proper metabolization of B
vitamins.
Lanosterol
Lanosterols exhibit strong cytotoxicity towards carcinoma
cells. It’s also an anti-bacterial, lowers cholesterol and
reduces candida.
Manganese
Manganese is a mineral and trace element that plays many
essential roles in the body. It aids in the metabolism of
food, normal functioning of the nervous system, in the
formation of the thyroxine hormone for the thyroid gland,
and in the production of sex hormones. Manganese works as an
antioxidant to help prevent cancer and heart disease.
Manganese helps activate enzymes needed for use of biotin,
B-1 (thiamin), and vitamin C. It's important for the
formation of thyroxine, the main hormone of the thyroid
gland. Manganese is essential for proper digestion and the
metabolization of proteins. Manganese also plays an
important role in digestion and utilization of food,
reproduction, normal bone structure, and normal functioning
of the central nervous system.
Magnesium
Magnesium is the fourth most abundant mineral in the body
and is essential to good health. Approximately 50% of total
body magnesium is found in bone. The other half is found
predominantly inside cells of body tissues and organs. Only
1% of magnesium is found in blood, but the body works very
hard to keep blood levels of magnesium constant.
The crucial health benefits of magnesium include solving or
preventing osteoporosis, heart attacks, hypertension,
constipation, migraines, leg cramps, kidney stones,
gallstones and more. Magnesium is an essential part of the
alternative health approaches of alternative medicine.
Melanin
Melanin is a natural substance that gives color (pigment) to
hair, skin, and the iris of the eye. It is produced by cells
in the skin called melanocytes. Melanin also helps protect
the skin from the sun. Increased melanin protects those who
have it from short-term damage from the sun, as well as the
long-term signs of aging, such as age spots, deep wrinkles
and rough texture. Free radicals have been implicated as the
cause of widespread damage to human cells. Melanin plays a
role in free scavenging radicals and preventing skin damage
they can cause. It affects the delicately designed lipids
that hold moisture in the stratum corneum. This is the
outermost layer of the epidermis. If the skin loses its
moisture, it becomes rigid and cracks.
Pantothenic Acid
The health benefits of Vitamin B5 or Pantothenic Acid
include alleviation of conditions like asthma, hair loss,
allergies, stress and anxiety, respiratory disorders and
heart problems. Also, it helps to improve immunity,
osteoarthritis, ageing signs, resistance to various types of
infections, physical growth, and diabetes and skin
disorders. Vitamin B5 is widely known to be an obstacle to
serious mental states like stress and anxiety. A customary
diet must contain recommended amount of Vitamin B5 to ensure
good health and proper functioning of each body part. It
performs wide variety of functions in our body, starting
from production of neurotransmitter in brain to fabrication
of steroids to extraction of fats, proteins and other vital
nutrients. In a nutshell, the essence of Vitamin B5 pats
every important aspect of keeping a good health.
Phenols
Phenols are compounds found in a wide variety of foods
ranging from Chaga to olive oil to green tea and almonds.
The antioxidant and antibacterial properties of phenols
benefit a wide variety of diseases, including rheumatoid
arthritis and Alzheimer’s Disease. Phenols are thought to be
the primary health benefit of olive oil consumption, with
benefits seen for breast cell health, bone health, and
cholesterol health.
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is the second most abundant mineral in the body
and 85% of it is found in the bones. The rest of the body's
phosphorus is found in the blood, the fluid around and in
cells, and in various organs like the heart, kidneys, brain,
and muscles, where it is involved in many critical
functions. Its main purpose is for building strong bones and
teeth, but this mineral is used by practically every cell in
the body.
Phosphorus is involved in virtually all physiological
chemical reactions in the body, and calcium and Vitamin D
are essential to proper functioning of the phosphorus. This
mineral protects and strengthens cell membranes, assists
other nutrients, hormones, and chemicals in their bodily
processes, and is necessary for normal bone and tooth
structure. Phosphorus is needed for healthy nerve impulses,
normal kidney functioning, and the utilization of
carbohydrates, fats, and proteins for growth, maintenance,
and repair of cells and for energy production. Phosphorus is
a component of DNA and RNA and serves in the preparation of
glucose for energy formation.
Phytonutrients
Apart from the major food principles like protein,
carbohydrates, and fats, large number of food items we
consume consists of invaluable components in them known as
phytonutrients or plant derived chemical substances.
Although their caloric value is insignificant, inclusion in
our diet in adequate levels is imperative since the
potential benefits in terms of direct contribution to health
promotion and disease prevention are enormous.
Studies have found that certain chemicals other than
nutritional principles in them have anti-mutagenic, free
radical scavenging and immunity boosting functions, which
help promote health and prevent diseases, over and above
their nutritive value. Phytonutrients are present abundantly
in the plant world.
Examples include:
1. Anti-oxidants 2. Phyto-sterols (plant sterols) 3.
Non-digestible carbohydrates such as tannins, pectin,
cellulose and mucilage 4. Natural acids 5. Enzymes and
lecithin.
Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides have many chains and must be broken down
into smaller portions before they can be fully digested.
Although polysaccharides are a form of sugar, many of their
food sources rarely taste sweet.
Polysaccharides are important in the prevention of
degenerative type diseases. These include cardiovascular
disease and diabetes type 2. Tea action is related to the
poly-phenols and polysaccharides parts of tea.
Polysaccharides can also act as an anticoagulant. It reduces
the stickiness of platelets making it harder for them to
build up in artery walls. They have anti-thrombotic effects
and blood lipids are reduced. HDL cholesterol may be raised
while LDL levels are decreased.
Polysaccharides help to regulate immune function with T and
B lymphocyte activation. It promotes Interferon, a white
cell medium and tumor necrosis (death).
Tea polysaccharides have the following effects. They lower
blood pressure and increase coronary artery capacity. Blood
sugar levels are reduced which is a benefit in treating
Diabetics. There is improved Beta cell function in the
pancreas, as well as anti-diabetic properties.
Anti-radiation effects may be noted, and free radicals can
be all but eliminated. There is anti-viral activity, and it
improves blood reproduction and maintenance.
Potassium
Potassium, the third most abundant mineral in human body, is
the synonym for health insurer. It contains the qualities
for maintaining a high level of human well-being and a
cheerful lifestyle. There is no way one should overlook the
inclusion of potassium in routine diet plan. Apart from
acting as an electrolyte, this mineral is required for
keeping heart, brain, kidney, muscle tissues and other
important organs of human body in good condition. Potassium
chloride is the main variety of this mineral amongst others.
It works in association with sodium to perform a number of
critical body tasks.
The health benefits of potassium include stroke, blood
pressure, anxiety and stress, muscular strength, metabolism,
heart and kidney disorders, water balance, electrolytic
functions, nervous system and other general health benefits
of potassium.
Saponins
Saponins are a group of chemicals with detergent-like
properties that plants produce to help them resist microbial
pathogens such as fungi.
Saponins may reduce elevated cholesterol levels by forming
complexes with cholesterol and bile acids, which prevents
them from being absorbed through your small intestines. The
cholesterol and bile complexes are excreted in the stool,
which lowers cholesterol levels in the blood and liver.
Saponins may decrease your risk of cancer. A 2004 study
published in "Journal of Medicinal Food" says colon, breast,
uterine and prostate cancer rates are lower in countries
where inhabitants consume large amounts of legumes. This may
be due to the immune system modulating effects of saponins
that increase anti-tumor activity in your body. The
stimulation of bile acid secretion in the intestinal tract,
and antioxidant activity may also contribute to a reduced
risk of cancer.
Antioxidants prevent cell damage by protecting lipids from
free radical oxidation reactions. Saponins prevent oxidation
of cholesterol in the colon, which may also help to reduce
colon damage and the risk of cancer. They also prevent
degeneration of DNA and protect cell proteins from free
radical damage.
Saponins may stimulate the immune system, and according to
the 2004 article referenced earlier, they are used as
adjuvants in vaccines and oral intakes of saponins have been
used to help treat retroviral infection. They stimulate
antibody production, inhibit viruses, and induce the
response by lymphocytes, which are white blood cells that
fight infection.
Selenium
Selenium is a trace element found in soil and is required to
maintain good health in trace amounts.
Selenium aids in many of the metabolic pathways and may help
treat prostate cancer; ongoing research is exploring the
relationship between low selenium levels and coronary heart
disease.
Selenium also benefits the skin during healing following
burn injuries. Shampoo with selenium may alleviate dandruff
problems. For skin care, selenium’s antioxidant properties
regenerate vitamins E and C, thereby decreasing the aging of
skin.
Major benefits of selenium have been found to improve the
immune system against bacterial and viral infections,
against cancer cells and herpes virus, cold sores, and
shingles. One of the major nutritional benefits of selenium
is increasing the HDL cholesterol to LDL cholesterol for a
healthy heart.
Sodium
Sodium occurs naturally in most foods. The most common form
of sodium is sodium chloride, which is table salt. Sodium is
an element that the body needs to function properly. The
body uses sodium to regulate blood pressure and blood
volume. Sodium is also critical for the functioning of
muscles and nerves.
Sterols
Plant sterols and stanols are naturally occurring substances
found in plants. Research has shown that plant sterols/stanols
included with a heart healthy eating plan may reduce your
risk for heart disease. The sterols/stanols work by blocking
the absorption of cholesterol in the small intestine. This
lowers the low density cholesterol known as the 'bad'
cholesterol (LDL ) by 6-15%, without lowering the good
cholesterol known as the high density cholesterol ( HDL).
Clinical research trials have documented safety and
effectiveness for use by the entire family. Plant stanols/sterols
do not interfere with cholesterol lowering medications.
Trametenolic Acid
Inotodiol and trametenolic acid are considered to be the
main bioactive compounds of the fruiting body of the
mushroom. These compounds show various biological
activities, including anti-tumour, anti-viral, hypoglycaemic,
anti-oxidant and cyto-protective.
Tripeptides
A tripeptide is a type of peptide that is formed when amino
acids link together in a specific order. Each tripeptide
contains three different amino acids. These amino acids are
joined by a peptide bond, which is a chemical bond that
occurs between two molecules. A common tripeptide is
isoleucine-proline-proline, also called the milk peptide,
which is responsible for keeping blood pressure low and
stable.
The main function of tripeptides is cell communication. They
also contribute to body functions such as blood pressure
regulation and thyroid function. As tripeptides age,
however, communication signals may start to deteriorate,
which can cause signs of aging and other health issues.
Another type of tripeptide is glutathione which is an
anti-oxidant that can be critical in protecting healthy
cells from free radicals in the body. Free radicals can
cause cell damage that is linked to the development of
cancer cells. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) is a
tripeptide responsible for regulating the release of
hormones in the thyroid.
Tripeptides have become popular with cosmetic companies who
are creating anti-aging products. Since the body uses
tripeptides for communication, anti-aging proponents believe
that topical forms of tripeptides can boost skin function
and reverse damage to the skin. This essentially gives cells
back their youth and prevents improper cell communication in
the skin. Anti-aging product manufactures claim that
tripetides used in these products improve the skin’s
appearance, making it smooth and soft.
Tripeptide-3 and tripeptide-1 are the common ingredients
used in these products, and are believed to stimulate skin
cells and produce more collagen. Due to the fact that
tripeptides usually are not cheap to produce, consumers
typically can expect to pay larger sums for products with
these active ingredients.
Triterpenes
Triterpenes are found in all living organisms: plants,
animals, humans. Triterpenes are precursors to steroids – in
order to produce steroids, the organism, whether plant or
animal produces triterpenes. Naturally occurring precursors
to steroids and naturally occurring steroids are the plant
and animal worlds’ way of managing inflammation, safely and
naturally. Triterpenes belong to a large group of compounds
arranged in a four or five ring configuration of 30 carbons
with several oxygens attached. Triterpenes are assembled
from a C5 isoprene unit through the cytosolic mevalonate
pathway to make a C30 compound and are steroidal in nature.
Cholesterol is one example of a triterpene. Phytosterols and
phytoecdysteroids are also triterpenes. The triterpenes are
subdivided into some 20 groups, depending on their
particular structures. Though all terpenoid compounds have
bioactivity in mammals, it is the triterpenes that are most
important to the adaptogenic effect found in plants such as
Chaga, ginseng or Eleutherococcus senticosus.
Triterpenoids
Triterpenoid saponins are triterpenes which belong to the
group of saponin compounds.
Triterpenoids Display Single Agent Anti-tumor Activity in a
Transgenic Mouse Model of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and
Small B Cell Lymphoma.
Vanillic Acid
Vanillic acid is a benzoic acid derivative used as a
flavoring agent. It is an oxidized form of vanillin produced
during the conversion of vanillin to ferulic acid. The
highest quantity of vanillic acid in plants has been found
in the roots of Angelica sinensis, which is used in
traditional Chinese medicine. Various studies have provided
evidence of the effectiveness of vanillic acid in the
management of immune or inflammatory responses. For
instance, vanillic acid enhanced the activity of human
lymphocyte proliferation and secretion of interferon-gamma
in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Another study
has shown that vanillic acid has a hepatoprotective effect
through its suppressive action on immune-mediated liver
inflammation in concanavalin A-induced liver injury.
However, it remains to be determined whether vanillic acid
has an anti-colitic effect.
A study on was done to determine whether vanillic acid has
beneficial effects against dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced
ulcerative colitis. The results showed that vanillic acid
reduced the severity of the clinical signs of DSS-induced
colitis, including weight loss and shortening of colon
length, and the disease activity index. The results of this
study showed that vanillic acid significantly suppressed the
expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and the activation of
transcription nuclear factor-B p65 in DSS treated colon
tissues. In addition, we observed that the plasma levels of
interleukin (IL)-6 were higher in the DSS-treated group than
in the control group, but these increased levels were
reduced by the administration of vanillic acid. Taken
together, these findings suggest that vanillic acid has a
beneficial effect on DSS-induced ulcerative colitis, thereby
indicating its usefulness in the regulation of chronic
intestinal inflammation.
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) is a vitamin that is required by your
body to turn carbohydrates into a form of energy usable
within your cells.
Thiamine is also used for digestive problems including poor
appetite, ulcerative colitis, and ongoing diarrhea.
Thiamine is also used for AIDS and boosting the immune
system, diabetic pain, heart disease, alcoholism, aging, a
type of brain damage called cerebellar syndrome, canker
sores, vision problems such as cataracts and glaucoma,
motion sickness, and improving athletic performance. Other
uses include preventing cervical cancer and progression of
kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Some people use thiamine for maintaining a positive mental
attitude; enhancing learning abilities; increasing energy;
fighting stress; and preventing memory loss, including
Alzheimer's disease.
Healthcare providers give thiamine shots for a memory
disorder called Wernicke's encephalopathy syndrome, other
thiamine deficiency syndromes in critically ill people,
alcohol withdrawal, and coma.
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
Riboflavin (vitamin B2) is manufactured in the body by the
intestinal flora and is easily absorbed, although very small
quantities are stored, so there is a constant need for this
vitamin. It is required by the body to use oxygen and the
metabolism of amino acids, fatty acids, and carbohydrates.
Riboflavin is further needed to activate vitamin B6
(pyridoxine), helps to create niacin and assists the adrenal
gland. It may be used for red blood cell formation, antibody
production, cell respiration, and growth. Riboflavin is used
for preventing low levels of riboflavin (riboflavin
deficiency), cervical cancer, and migraineheadaches. It is
also used for treating riboflavin deficiency, acne, muscle
cramps, burning feet syndrome, carpal tunnel syndrome, and
blood disorders such as congenital methemoglobinemia and red
blood cell aplasia. Some people use riboflavin for eye
conditions including eye fatigue, cataracts, and glaucoma.
Other uses include increasing energy levels; boosting immune
system function; maintaining healthy hair, skin, mucous
membranes, and nails; slowing aging; boosting athletic
performance; promoting healthy reproductive function; canker
sores; memory loss, including Alzheimer's disease; ulcers;
burns; alcoholism; liver disease; sickle cellanemia; and
treating lactic acidosis brought on by treatment with a
class of AIDS medications called NRTI drugs.
Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
Niacin also called nicotinic acid, niacinamide or nicotinic
acid and referred to as vitamin B 3, which can be
manufactured by the body. Niacin is derived from two
compounds - nicotinic acid and niacinamide. Vitamin B3 is
required for cell respiration, helps in the release of
energy and metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins,
proper circulation and healthy skin, functioning of the
nervous system, and normal secretion of bile and stomach
fluids. It is used in the synthesis of sex hormones,
treating schizophrenia and other mental illnesses, and a
memory-enhancer.
Vitamin D2 (Ergosterol)
Ergosterol is a biological precursor (a provitamin) to
vitamin D2. It is turned into viosterol by ultraviolet
light, and is then converted into ergocalciferol, a form of
vitamin D also known as D2 or D2.[1] For this reason, when
yeast (such as brewer's yeast) and fungi (such as
mushrooms), are exposed to ultraviolet light, significant
amounts of vitamin D2 are produced.
Because ergosterol is present in cell membranes of fungi yet
absent in those of animals, it is a useful target for
antifungal drugs. Ergosterol is also present in the cell
membranes of some protists, such as trypanosomes. The three
major human diseases caused by trypanosomatids are; African
trypanosomiasis (Sleeping Sickness, caused by Trypanosoma
brucei), South American trypanosomiasis (Chagas Disease,
caused by Trypanosoma cruzi), and leishmaniasis (a set of
trypanosomal diseases caused by various species of
Leishmania). This is the basis for the use of some
antifungals against West African sleeping sickness.
Vitamin K
Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin, so your body stores it
in fat tissue and the liver. What can high-vitamin K foods
do for you?
• Allow your blood to clot normally • Help protect your
bones from fracture • Help prevent postmenopausal bone loss
• Help prevent calcification of your arteries • Provide
possible protection against liver and prostate cancer
Zinc
Zinc is a metal. It is called an “essential trace element”
because very small amounts of zinc are necessary for human
health.
Zinc is used for treatment and prevention of zinc deficiency
and its consequences, including stunted growth and acute
diarrhea in children, and slow wound healing.
It is also used for boosting the immune system, treating the
common cold and recurrent ear infections, and preventing
lower respiratory infections. It is also used for malaria
and other diseases caused by parasites.
Some people use zinc for an eye disease called macular
degeneration, for night blindness, and for cataracts. It is
also used for asthma; diabetes; high blood pressure;
acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS); and skin
conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, and acne.
Other uses include treating attention deficit-hyperactivity
disorder (ADHD), blunted sense of taste (hypogeusia),
ringing in the ears (tinnitus), severe head injuries,
Crohn’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, Down syndrome,
Hansen’s disease, ulcerative colitis, peptic ulcers and
promoting weight gain in people with eating disorders such
as anorexia nervosa.
Some people use zinc for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH),
male infertility, erectile dysfunction (ED), weak bones
(osteoporosis), rheumatoid arthritis, and muscle cramps
associated with liver disease. It is also used for sickle
cell disease and inherited disorders such as acrodermatitis
enteropathica, thalassemia, and Wilson’s disease.
Some athletes use zinc for improving athletic performance
and strength.
Zinc is also applied to the skin for treating acne, aging
skin, herpes simplex infections, and to speed wound healing.
The following are purported uses of the Chaga
Mushroom:
• Anti-aging
• Anti-allergic
• Anti-bacterial
• Anti-Cancer
• Anti-genotoxicity
• Anti-inflammatory
• Anti-microbial
• Anti-mutagenic
• Anti-oxidant
• Anti-tumor
• Anti-viral
• Arthritis
• Asthma
• Bacterial Diseases
• Blood Pressure High (Hypertension)
• Blood Pressure Low (Hypotension)
• Blood Purification
• Bronchitis
• Candidiasis (yeast)
• Cardio-Vascular
• Crohn’s Disease (CD)
• Diabetes
• Fungal Growth
• Gastritis
• Heart Disease
• Hepatoprotective
• HIV
• Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
• Immune Support / Enhancer
• Influenza
• Intestinal Worms
• Kidney Tonic
• Lower Cholesterol
• Liver / Hepatitis
• Pain Relief
• Parasites
• Parotid gland
• Pulmonary Diseases
• Skin Ailments
• Stomach Ailments
• Stomach Disease
• Tuberculosis
• Ulcerative Colitis (UC)
Buy Pure wild Harvested Chaga mushroom Tea
click here